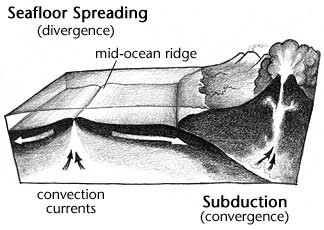
Seafloor spreading is the continuous process of forming new igneous rock at midocean ridges by injection of magma that forms new seafloor.
Sea floor spreading and subduction animation.
Have you noticed lately that your students just aren t listening when you try to teac.
I m sorry you somehow found this.
Seafloor spreading and plate boundaries.
That is the time it takes for new rock to form at the mid ocean ridge move atoss the ocean and sink into a trench.
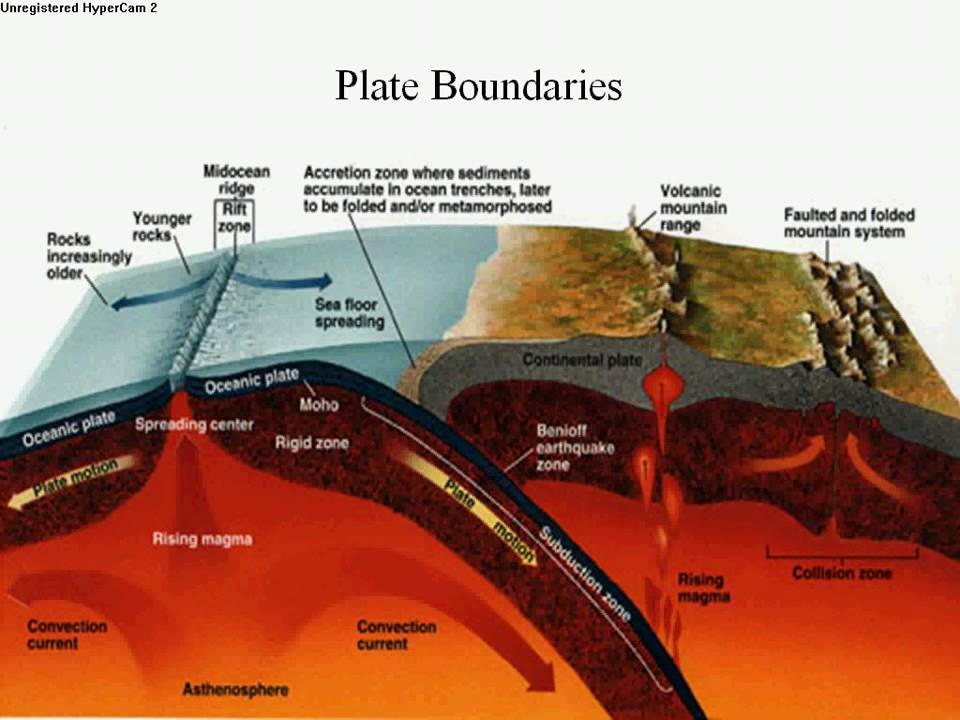
Seafloor spreading is one of the two major processes of plate tectonics the other being subduction.
At subduction zones the edge of the denser plate subducts or slides beneath the less dense one.
Spreading rate is the rate at which an ocean basin widens due to seafloor spreading.
The denser lithospheric material then melts back into the earth s mantle.
The rate at which new oceanic lithosphere is added to each tectonic plate on either side of a mid ocean ridge is the spreading half rate and is equal to half of the spreading rate.
Spreading rates determine if the ridge is fast intermediate or slow.
Seafloor spreading is just one part of plate tectonics.
I didn t know it would come to this.
As upwelling of magma continues the plates continue to diverge a process known as seafloor spreading samples collected from the ocean floor show that the age of oceanic crust increases with distance from the spreading centre important evidence in favour of this process.
Trenches accretionary wedges prisms and volcanic or island arcs are key surface features produced by subduction.
A subduction zone is the entire area of subduction between the trench and the volcanic arc.
Because of these processes the ocean floor is renewed about every 200 million years.
This animation depicts a 100 000 year time span of seafloor spreading.
The process of subduction and sea floor spreading can change the size and shape of the oceans.
It also shows the subduction of oceanic crust under continental crust and the resulting formation of magma and subsequent volcanism.
These age data also allow the rate of seafloor spreading to be determined and they show that rates.
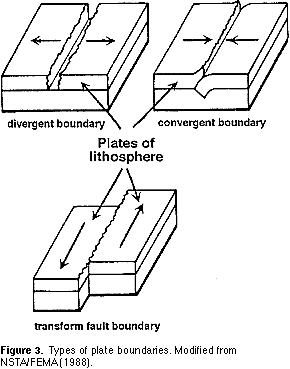
This report describes how to build a model of the outer 300 km 180 miles of the earth that can be used to develop a better understanding of the principal features of plate tectonics including sea floor spreading the pattern of magnetic stripes frozen into the sea floor transform faulting thrust faulting subduction and volcanism.